
为了近距离检查 Kubernetes API 对象,我们需要一个具体的例子。让我们以 Node 对象为例,它应该很容易理解,因为它代表了您可能比较熟悉的东西——集群中的一台计算机。
我用 kind 工具配置的 Kubernetes 集群有三个节点——一个 master 和两个 worker。它们由 API 中的三个 Node 对象表示。我可以使用 查询 API 并列出这些对象 kubectl get nodes。
kubectl get nodes
# output
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
kind-control-plane Ready control-plane 13h v1.25.3
kind-worker Ready <none> 13h v1.25.3
kind-worker2 Ready <none> 13h v1.25.3
下图显示了三个 Node 对象和组成集群的实际集群机器。每个 Node 对象实例代表一个主机。在每个实例中,Spec 包含主机的(一部分)配置,而 Status 包含主机的状态。
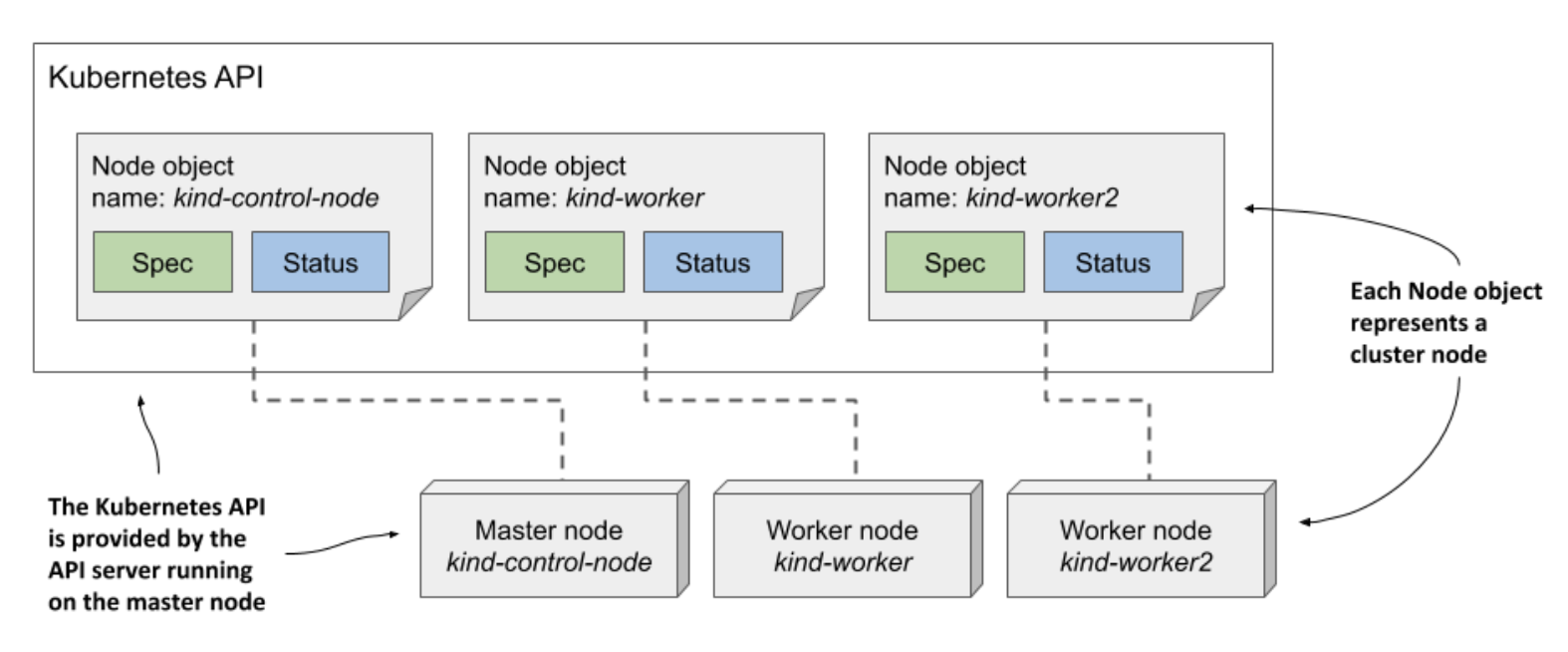
节点对象与其他对象略有不同,因为它们通常由 Kubelet(运行在集群节点上的节点代理)而不是用户创建。当您将机器添加到集群时,Kubelet 通过创建代表主机的 Node 对象来注册节点。然后,用户可以编辑
Spec中的一部分字段。
让我们仔细看看其中一个 Node 对象。通过运行命令列出集群中的所有节点对象,kubectl get nodes 然后选择一个您要检查的对象。然后,执行kubectl get node <node-name> -o yaml命令(使用 -o json 则表示输出 json 格式的文档),在其中替换<node-name>为节点的名称,如下面的清单所示。
kubectl get node kind-control-plane -o yaml
#A The Type Metadata specifies the type of object and the API version of this object manifest.
apiVersion: v1 #A
kind: Node #A
metadata: # The Object Metadata section begins here
annotations: ...
creationTimestamp: "2020-05-03T15:09:17Z"
labels: ...
managedFields: ...
name: kind-control-plane #C The object name (the node’s name)
resourceVersion: "3220054"
selfLink: /api/v1/nodes/kind-control-plane
uid: 16dc1e0b-8d34-4cfb-8ade-3b0e91ec838b
spec:
#E The IP range reserved for the pods on this node
podCIDR: 10.244.0.0/24 #E
podCIDRs: #E
- 10.244.0.0/24 #E
taints:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
# The node’s actual state is shown in the status section, which begins here and extends to the end of this listing
status:
#G The IP(s) and hostname of the node
addresses: #G
- address: 172.18.0.2 #G
type: InternalIP #G
- address: kind-control-plane #G
type: Hostname #G
allocatable: ...
#H The nodes capacity (the amount of compute resources it has)
capacity: #H
cpu: "8" #H
ephemeral-storage: 401520944Ki #H
hugepages-1Gi: "0" #H
hugepages-2Mi: "0" #H
memory: 32720824Ki #H
pods: "110" #H
conditions:
- lastHeartbeatTime: "2020-05-17T12:28:41Z"
lastTransitionTime: "2020-05-03T15:09:17Z"
message: kubelet has sufficient memory available
reason: KubeletHasSufficientMemory
status: "False"
type: MemoryPressure
...
daemonEndpoints:
kubeletEndpoint:
Port: 10250
#I The list of cached container images on this node
images: #I
- names: #I
- k8s.gcr.io/etcd:3.4.3-0 #I
sizeBytes: 289997247 #I
... #I
#J Information about the node’s operating system and the Kubernetes components running on it
nodeInfo: #J
architecture: amd64 #J
bootID: 233a359f-5897-4860-863d-06546130e1ff #J
containerRuntimeVersion: containerd://1.3.3-14-g449e9269 #J
kernelVersion: 5.5.10-200.fc31.x86_64 #J
kubeProxyVersion: v1.18.2 #J
kubeletVersion: v1.18.2 #J
machineID: 74b74e389bb246e99abdf731d145142d #J
operatingSystem: linux #J
osImage: Ubuntu 19.10 #J
systemUUID: 8749f818-8269-4a02-bdc2-84bf5fa21700 #J
在清单中,对象定义的四个主要部分和节点的更重要的属性都进行了注释,以帮助您区分更重要和不太重要的字段。省略了一些行以减少清单的长度。
现在让我们仔细看看四个主要部分中的每个字段。
如您所见,清单以 apiVersion 和 kind 字段开头,它们指定了此对象的 API 版本和类型。 apiVersion 用于描述此对象的概要。如前所述,一个对象类型可以与多个概要相关联,在每个概要中通过的不同字段描述对象。但是,通常每个类型只存在一个概要。
apiVersion 在之前清单中的 是 v1 ,但您将接下来看到 apiVersion ,其他对象类型中不仅仅包含版本号。例如,对于 Deployment 对象,apiVersion 是 apps/v1({group}/{version})。而该字段最初仅用于指定 API 版本,现在也用于指定资源所属的 API 组。Node 对象 属于核心 API 组,通常从该 apiVersion 字段中省略。
清单中定义的对象类型由字段 kind 指定。前一个清单中的对象类型是 Node . 在前面的实践中,您曾经创建了 Deployment、Service 和 Pod 类型的对象。
该 metadata 部分包含此对象实例的元数据。它包含实例的 name ,以及附加属性,如labels和annotations,以及`resourceVersion,managedFields,和其他低级字段,这些字段将在后续文章进行解释。
spec 是特定于每种对象类型的部分。与其他对象类型相比,Node 对象的 spec 相对较短。
podCIDR 字段指定分配给节点的 pod IP 范围。在这个节点上运行的 Pod 被分配了这个范围内的 IP。taints 字段并不重要,但您将在第 18 章中了解它。通常,对象的 spec 部分包含了许多用于配置对象的字段。
该 status 部分在不同类型的对象之间也有所不同,但其目的始终相同 - 它包含对象所代表的事物的最后被观察的状态。
对于 Node 对象,状态显示节点的
IP address(es)
hostname
提供计算资源的能力
节点的当前状况
它已经下载并现在在本地缓存的容器映像
有关其运行的系统信息
它运行的 Kubernetes 组件的版本
要了解清单中各个字段的更多信息,您可以参考 http://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/ 上的 API 参考文档或使用kubectl explain如下所述的命令。
kubectl 工具有一个很好的功能,它允许您从命令行查找每个对象类型(kind)的每个字段的解释。通常,您首先通过运行要求它提供对象种类的基本描述 kubectl explain <kind> ,如下所示:
kubectl explain nodes
# output
KIND: Node
VERSION: v1
DESCRIPTION:
Node is a worker node in Kubernetes. Each node will have a unique
identifier in the cache (i.e. in etcd).
FIELDS:
apiVersion <string>
APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an
object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal
value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
kind <string>
Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object
represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits
requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
metadata <Object>
Standard object's metadata. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata
spec <Object>
Spec defines the behavior of a node.
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
status <Object>
Most recently observed status of the node. Populated by the system.
Read-only. More info:
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
该命令打印对象的解释并列出对象可以包含的顶级字段。
然后,您可以更深入地查找每个特定字段下的子字段。例如,您可以使用以下命令来解释节点的spec字段:
kubectl explain node.spec
# output
KIND: Node
VERSION: v1
RESOURCE: spec <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
Spec defines the behavior of a node.
https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
NodeSpec describes the attributes that a node is created with.
FIELDS:
configSource <Object>
Deprecated: Previously used to specify the source of the node's
configuration for the DynamicKubeletConfig feature. This feature is removed
from Kubelets as of 1.24 and will be fully removed in 1.26.
externalID <string>
Deprecated. Not all kubelets will set this field. Remove field after 1.13.
see: https://issues.k8s.io/61966
podCIDR <string>
PodCIDR represents the pod IP range assigned to the node.
podCIDRs <[]string>
podCIDRs represents the IP ranges assigned to the node for usage by Pods on
that node. If this field is specified, the 0th entry must match the podCIDR
field. It may contain at most 1 value for each of IPv4 and IPv6.
providerID <string>
ID of the node assigned by the cloud provider in the format:
<ProviderName>://<ProviderSpecificNodeID>
taints <[]Object>
If specified, the node's taints.
unschedulable <boolean>
Unschedulable controls node schedulability of new pods. By default, node is
schedulable. More info:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/nodes/node/#manual-node-administration
请注意顶部给出的 API 版本。如前所述,可以存在多个相同类型的版本。不同的版本可以有不同的字段或默认值。如果要显示不同的版本,请使用--api-version选项指定它。
spec 和部分中的字段集 status 对于每种对象类型都是不同的,但 conditions 在许多对象中都可以找到该字段。它列出了对象当前所处的条件。当您需要对对象进行故障排除时,它们非常有用,因此让我们更仔细地检查它们。
以 Node 对象为例,本节还教您如何轻松识别集群节点的问题。
让我们再次打印出其中一个节点对象的 YAML 清单,但这次我们将只关注对象的 status 下的 conditions 字段。
要运行的命令及其输出如下:
$ kubectl get node kind-control-plane -o yaml
# output
...
status:
...
conditions:
- lastHeartbeatTime: "2020-05-17T13:03:42Z"
lastTransitionTime: "2020-05-03T15:09:17Z"
message: kubelet has sufficient memory available
reason: KubeletHasSufficientMemory
status: "False"
type: MemoryPressure
- lastHeartbeatTime: "2020-05-17T13:03:42Z"
lastTransitionTime: "2020-05-03T15:09:17Z"
message: kubelet has no disk pressure
reason: KubeletHasNoDiskPressure
status: "False"
type: DiskPressure
- lastHeartbeatTime: "2020-05-17T13:03:42Z"
lastTransitionTime: "2020-05-03T15:09:17Z"
message: kubelet has sufficient PID available
reason: KubeletHasSufficientPID
status: "False"
type: PIDPressure
- lastHeartbeatTime: "2020-05-17T13:03:42Z"
lastTransitionTime: "2020-05-03T15:10:15Z"
message: kubelet is posting ready status
reason: KubeletReady
status: "True"
type: Ready
TIP
jq命令可以非常方便的帮助您查看对象结构的一部分。例如,要显示节点的状态条件,您可以运行kubectl get node <name> -o json | jq .status.conditions.YAML 的等效命令是
yq.
有四个条件可以显示节点的状态。每个条件都有一个 type 和一个 status 字段,可以是 True,False 或 Unknown,如图所示。条件字段:
reason 是一个面向机器的字段,表示最后一次状态转换的原因message 是一个带有转换详细信息的面向用户的字段,表示最后一次状态转换的原因lastTransitionTime 字段表明条件何时从一种状态转移到另一种状态lastHeartbeatTime 字段显示控制器最后一次接收到给定条件的更新的时间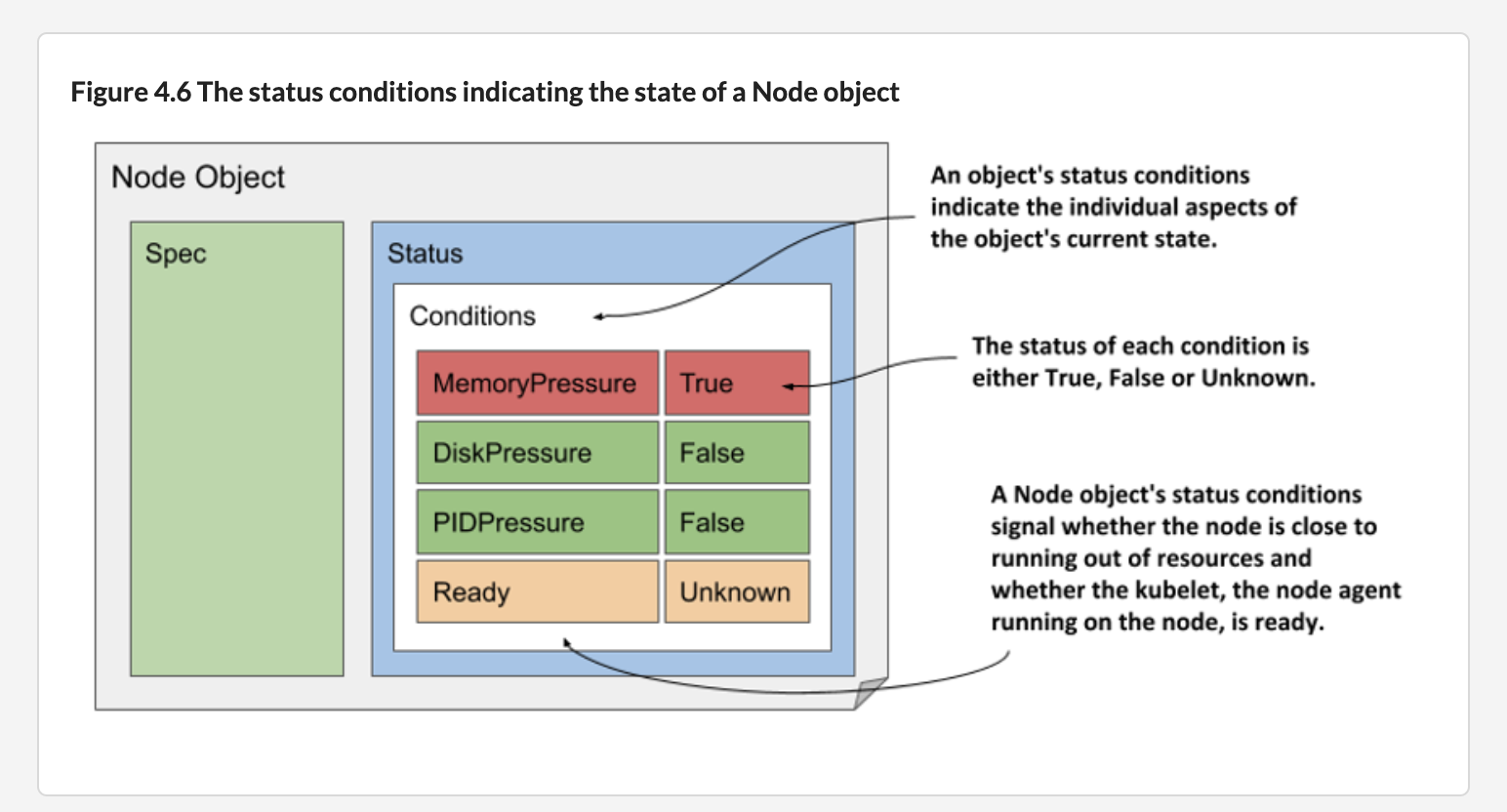
尽管它是列表中的最后一个条件,但该 Ready 条件可能是最重要的,因为它表明节点是否准备好接受新的工作负载(pod)。其他条件( MemoryPressure 、 DiskPressure 和 PIDPressure )表示节点是否资源不足。如果节点开始出现异常行为,请记住检查这些条件 - 例如,如果在其上运行的应用程序开始耗尽资源或崩溃。
诸如 Node 对象 中的条件列表也用于许多其他对象类型。前面解释的条件很好地说明了,为什么大多数对象的状态由条件列表表示,而不是用单个字段表示。如果将对象的状态表示为单个字段,则随后使用新值对其进行扩展将非常困难,因为这将需要更新所有监视这个状态,并基于它执行操作的客户端。一些对象类型最初使用单个字段,有些仍然使用,但现在大多数使用条件列表。
注意
条件通常是相互独立的,这意味着它们分别代表对象不相关的方面。
本节重点是介绍 Kubernetes API 对象的共同特性,所以我们只关注 conditions 字段,但它远不是 Node 对象 状态中唯一的字段。要探索其他内容,请使用 kubectl explain 前面边栏中所述的命令。
笔记
作为练习,使用该命令
kubectl get <kind> <name> -o yaml来探索您迄今为止创建的其他对象(部署、服务和 pod)。
为了让您对 Kubernetes API 对象的整个结构有一个正确的印象,有必要向您展示一个对象的完整 YAML 清单。虽然我个人经常使用这种方法来检查对象,但检查对象的更用户友好的方法是 kubectl describe 命令,它通常显示相同的信息,有时甚至更多。
让我们尝试 kubectl describe 在 Node 对象上运行命令。为了让事情变得有趣,让我们用它来描述一个工作节点而不是主节点。这是命令及其输出:
kubectl describe node kind-worker-2
# output
Name: kind-worker2
Roles: <none>
Labels: beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
beta.kubernetes.io/os=linux
kubernetes.io/arch=amd64
kubernetes.io/hostname=kind-worker2
kubernetes.io/os=linux
Annotations: kubeadm.alpha.kubernetes.io/cri-socket: /run/contain...
node.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl: 0
volumes.kubernetes.io/controller-managed-attach-deta...
CreationTimestamp: Sun, 03 May 2020 17:09:48 +0200
Taints: <none>
Unschedulable: false
Lease:
HolderIdentity: kind-worker2
AcquireTime: <unset>
RenewTime: Sun, 17 May 2020 16:15:03 +0200
Conditions:
Type Status ... Reason Message
---- ------ --- ------ -------
MemoryPressure False ... KubeletHasSufficientMemory ...
DiskPressure False ... KubeletHasNoDiskPressure ...
PIDPressure False ... KubeletHasSufficientPID ...
Ready True ... KubeletReady ...
Addresses:
InternalIP: 172.18.0.4
Hostname: kind-worker2
Capacity:
cpu: 8
ephemeral-storage: 401520944Ki
hugepages-1Gi: 0
hugepages-2Mi: 0
memory: 32720824Ki
pods: 110
Allocatable:
...
System Info:
...
PodCIDR: 10.244.1.0/24
PodCIDRs: 10.244.1.0/24
Non-terminated Pods: (2 in total)
Namespace Name CPU Requests CPU Limits ... AGE
--------- ---- ------------ ---------- ... ---
kube-system kindnet-4xmjh 100m (1%) 100m (1%) ... 13d
kube-system kube-proxy-dgkfm 0 (0%) 0 (0%) ... 13d
Allocated resources:
(Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.)
Resource Requests Limits
-------- -------- ------
cpu 100m (1%) 100m (1%)
memory 50Mi (0%) 50Mi (0%)
ephemeral-storage 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
hugepages-1Gi 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
hugepages-2Mi 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Starting 3m50s kubelet, kind-worker2 ...
Normal NodeAllocatableEnforced 3m50s kubelet, kind-worker2 ...
Normal NodeHasSufficientMemory 3m50s kubelet, kind-worker2 ...
Normal NodeHasNoDiskPressure 3m50s kubelet, kind-worker2 ...
Normal NodeHasSufficientPID 3m50s kubelet, kind-worker2 ...
Normal Starting 3m49s kube-proxy, kind-worker2 ...
如您所见,该 kubectl describe 命令显示了您之前在 Node 对象的 YAML 清单中找到的所有信息,但以更易读的形式显示。您可以看到名称、IP 地址和主机名,以及节点的条件和可用容量。
除了 Node 对象 本身存储的信息外,该 kubectl describe 命令还显示节点上运行的 pod 以及分配给它们的计算资源总量。下面也是与节点相关的事件列表。
此附加信息不在 Node 对象 本身中找到,而是由 kubectl 工具从其他 API 对象中收集的。例如,节点上运行的 pod 列表是通过pods 资源获取 Pod 对象 获得的。
如果您自己运行 describe 命令,则可能不会显示任何事件。这是因为只显示最近发生的事件。对于 Node 对象,除非节点存在资源容量问题,否则只有在您最近(重新)启动节点时才会看到事件。
几乎每个 API 对象类型都有与之关联的事件。由于它们对于调试集群至关重要,因此在您开始探索其他对象之前,它们需要仔细查看。
好好学习,天天向上